Arnold Press
Exercise / Shoulders
Arnold Press
The Arnold Press is a popular strength training exercise that was developed by Arnold Schwarzenegger in the 1970s. This exercise is a variation of the traditional shoulder press, and involves a rotational movement that targets multiple muscles in the shoulders, triceps, and upper back. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the Arnold Press, including its benefits, technique, and variations.
How to do :

following these tips and tricks
- Starting Position: Position yourself on the bench and hold a dumbbell in each hand at chest height. In the starting position, your back should be straight, the dumbbells should be at shoulder level and the palms should be facing the body.
- Form: Make sure that your palms are facing your body and your elbows are bent. Your arms should be in close to your torso.
- Making sure you are inhaling, raise the dumbbells while at the same time turning your hands so that the palms now face outwards.
- Exhale slowly while continuing to raise the dumbbells until your arms are stretched above you and your elbows are locked.
- Pause for a count of two at the top of the movement, and then start to lower the dumbbells while inhaling. Lower the weight slowly and in a controlled manner with your palms facing your body.
- This, as before, has now become your starting position. Then raise the dumbbells as you rotate the palms of your hands until they are facing forward, keeping your elbows in. Do the required number of repetitions of the same movement.
Tips :
When performing the Arnold Press, it’s important to use proper technique to avoid injury and maximize results. Start with a lighter weight and gradually increase the weight as your strength improves. Ensure that you work slowly, and get a full 180 degree rotation going through both hands and arms.
When performing the Arnold Press, it’s important to use proper technique to avoid injury and maximize results. Start with a lighter weight and gradually increase the weight as your strength improves. Ensure that you work slowly, and get a full 180 degree rotation going through both hands and arms.
Benefits of the Arnold Press
- Targets deltoid muscles: The Arnold Press targets multiple muscles in the shoulders, including the anterior, medial, and posterior deltoids, as well as the triceps and upper back muscles. This means that you can achieve a more balanced and comprehensive shoulder workout by incorporating this exercise.
- Improves shoulder stability: The rotational movement of the Arnold Press requires more shoulder stability than other shoulder exercises, which can help reduce the risk of shoulder injuries and improve shoulder mobility.
- Enhances muscle symmetry: The rotational movement of the Arnold Press helps improve muscle symmetry and balance between the left and right sides of the body, which is important for overall strength and aesthetics.
- Adds variety to your routine: Including the Arnold Press in your shoulder routine can add variety and challenge to your workouts, which can help prevent boredom and plateauing.
- Can improve other lifts: The Arnold Press can help improve other lifts, such as the Overhead Press, by improving shoulder stability and strength.
Cons of Arnold Press:
- Requires proper technique: Like all weightlifting exercises, the Arnold Press requires proper technique to avoid injury and maximize results. It’s important to use a weight that is appropriate for your fitness level and to start with a lighter weight and gradually increase as your strength improves.
- Can be challenging for beginners: The rotational movement of the Arnold Press can be challenging for beginners, especially those who are new to weightlifting. It’s important to start with lighter weights and focus on proper form and technique.
- Not suitable for those with shoulder injuries: The Arnold Press can be too challenging for those with shoulder injuries or mobility issues. If you have a pre-existing condition, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before attempting this exercise.aesthetics.
- May not be suitable for all fitness goals: While the Arnold Press is an effective exercise for building overall upper body strength and improving shoulder stability, it may not be suitable for all fitness goals. For example, if your primary goal is to build muscle mass in the shoulders, other isolation exercises such as the lateral raise or front raise may be more effective.
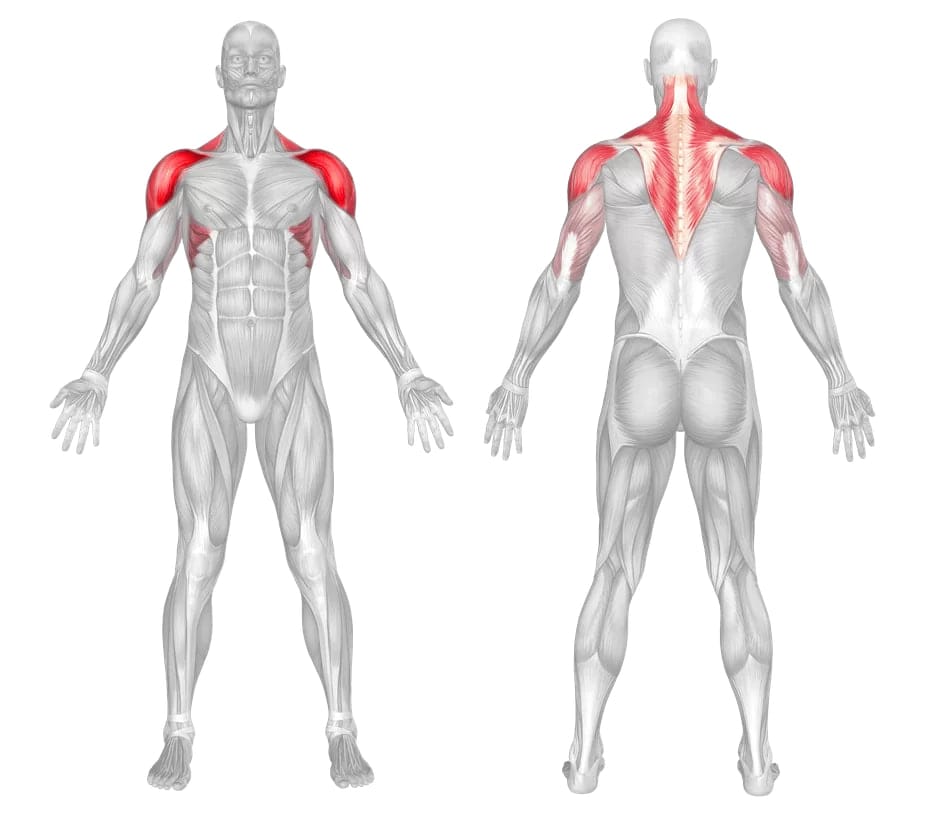
Arnold Press – Muscles Worked
Deltoids (anterior, medial, and posterior): The deltoids are the main target of the Arnold Press. The anterior deltoid helps lift the arm to the front of the body, while the medial and posterior deltoids help lift the arm to the side and back of the body, respectively.
Triceps: The triceps are the secondary muscles worked during the Arnold Press, as they help extend the arm during the upward phase of the movement.
Upper back muscles: The upper back muscles, including the rhomboids and traps, also assist in stabilizing the shoulders and maintaining proper form during the exercise.
Supraspinatus: The supraspinatus muscle is responsible for initiating the abduction of the arm, meaning it is activated when lifting the arm away from the body, as well as stabilizing the shoulder joint during movement. While the supraspinatus muscle is not directly targeted by the Arnold Press, it is involved in the movement of the shoulder joint and can be engaged to some degree as a stabilizer during the exercise.
Levator scapula: The levator scapula muscle works in conjunction with other muscles of the shoulder and neck to allow movement of the scapula, which is important for proper shoulder function. Although the levator scapula is not a primary muscle worked during the Arnold Press, it can be engaged to some degree as a stabilizer.
Serratus Anterior: The serratus anterior muscle plays an important role in scapular movement, as it is responsible for protracting (moving the scapula forward) and stabilizing the scapula against the rib cage. The serratus anterior, along with other muscles of the shoulder and upper back, can help to maintain proper scapular positioning during the exercise.
Triceps: The triceps are the secondary muscles worked during the Arnold Press, as they help extend the arm during the upward phase of the movement.
Upper back muscles: The upper back muscles, including the rhomboids and traps, also assist in stabilizing the shoulders and maintaining proper form during the exercise.
Supraspinatus: The supraspinatus muscle is responsible for initiating the abduction of the arm, meaning it is activated when lifting the arm away from the body, as well as stabilizing the shoulder joint during movement. While the supraspinatus muscle is not directly targeted by the Arnold Press, it is involved in the movement of the shoulder joint and can be engaged to some degree as a stabilizer during the exercise.
Levator scapula: The levator scapula muscle works in conjunction with other muscles of the shoulder and neck to allow movement of the scapula, which is important for proper shoulder function. Although the levator scapula is not a primary muscle worked during the Arnold Press, it can be engaged to some degree as a stabilizer.
Serratus Anterior: The serratus anterior muscle plays an important role in scapular movement, as it is responsible for protracting (moving the scapula forward) and stabilizing the scapula against the rib cage. The serratus anterior, along with other muscles of the shoulder and upper back, can help to maintain proper scapular positioning during the exercise.
0 %
Deltoid Anterior (Lateral and Posterior)
0 %
Synergists - Supraspinatus
0 %
Synergists - Trapezius
0 %
Synergists - Triceps Brachii
0 %
Synergists - Serratus Anterior
