Smith Machine Squat
Exercise List / Leg
Smith Machine Squat
The Smith machine squat is a controlled variation of the traditional squat. Unlike free-weight squats, the Smith Machine guides the movement path, allowing you to focus on proper technique and effectively target specific muscles. This feature can be especially beneficial for beginners or those needing additional support, as it reduces the demand for balancing the weight.
How to do :

following these tips and tricks
- Set Up the Smith Machine
- Position Yourself Under the Bar
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart.
- Position the bar across your shoulders and upper back (not on your neck).
- Place your hands on the bar just outside your shoulders and grip firmly.
- Foot Placement : For a standard squat, keep your feet directly under your body. For a glute-focused variation, move your feet forward slightly.
- Begin the Squat
- Unlock the bar by rotating it slightly forward or releasing the safety mechanism.
- Slowly lower yourself by bending at the knees and hips, keeping your chest lifted and core engaged. Aim to lower until your thighs are parallel to the ground or as deep as your flexibility allows.
- Drive Up
- Press through your heels to return to a standing position.
- Maintain control of the bar and avoid locking out your knees at the top.
Begin by positioning the bar at shoulder height. Set the safety catches slightly below your full squat depth to avoid overextending in case you need to bail.
Safety Tips for Smith Machine :
- Warm Up Properly: Warm up with light weights or bodyweight squats to activate your muscles and reduce the risk of injury.
- Maintain Proper Form: Keep your chest up, engage your core, and avoid rounding your lower back. Proper form is essential to avoid strain on your knees and spine.
- Placing the Bar Too High on Your Neck: Ensure the bar rests across your traps and shoulders, not directly on your neck, to prevent strain and discomfort.
- Avoid Going Too Heavy Too Soon: Start with a manageable weight, focusing on form before increasing your load.
- Use Safety Stops: Set the safety stops to catch the bar at the lowest point of your squat in case you need to bail.
Benefits of Machine Squat
- Stability and Safety
- The Smith machine provides stability, especially for beginners or those recovering from injury. The guided bar path reduces the risk of wobbling or tipping, allowing you to focus more on the movement and less on balance.
- The built-in safety stops are helpful if you’re lifting without a spotter. You can set the stoppers at your lowest range, so you don’t get pinned under the bar if you reach failure.
- Better Form Focus
- The Smith machine limits lateral movement, allowing you to concentrate on depth, positioning, and form without worrying about stabilizing the bar.
- This makes it easier to work on specific muscle activation and feel a better “mind-muscle connection,” especially with the quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
- Increased Muscle Activation for Beginners
- For beginners, the Smith machine squat can be a useful way to learn and build strength. With added stability, they can use slightly heavier weights without risking poor form, building strength before transitioning to free barbell squats.
- Isolation of Targeted Muscle Groups
- The Smith machine squat is ideal for isolating specific muscle groups, as the bar path is fixed. This lets you adjust your body position to focus on specific muscles, like the quads, glutes, or hamstrings, with greater control.
- Effective for High-Volume Training
- The machine is great for high-rep sets or drop sets, especially if you’re training for hypertrophy. The fixed path makes it easier to grind out high reps with less mental focus on balance, so you can push the muscle to fatigue safely.
- Reduced Strain on Lower Back
- Since the bar path is fixed, it helps keep your posture more upright, reducing the need for a forward lean that might strain the lower back, especially for those with limited mobility or lower back issues.
Muscles Worked
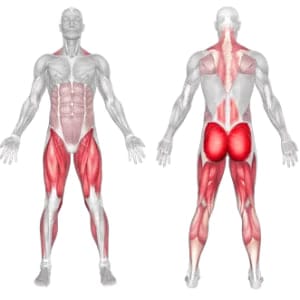
0 %
Target - Quadriceps
0 %
Synergists - Gluteus Maximus
0 %
Synergists - Adductor Magnus
0 %
Synergists - Soleus
0 %
Stabilizers - Erector Spinae
